Small animal imaging in vivo
Small animal imaging refers to the qualitative and quantitative research on the cellular and molecular level of biological processes in vivo by means of imaging, which can be mainly divided into optical imaging, nuclide imaging, magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasonic imaging and CT imaging.
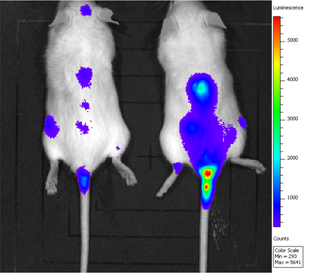
Its advantage is that it can reflect the spatial and temporal distribution of cell or gene expression, so as to understand the relevant biological processes, specific gene functions and interactions in active objects. The research object can be tracked repeatedly for a long time to improve the comparability of data and avoid the impact of individual differences on the experimental results. In addition, there is no need to kill the experimental object, so as to save the experimental cost.


